The Cloud Seeding Conundrum: A Scientific Exploration of Weather Modification
Related Articles: The Cloud Seeding Conundrum: A Scientific Exploration of Weather Modification
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Cloud Seeding Conundrum: A Scientific Exploration of Weather Modification. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Cloud Seeding Conundrum: A Scientific Exploration of Weather Modification

The ability to control the weather has long captivated the human imagination. From ancient rain dances to modern cloud seeding experiments, the pursuit of influencing precipitation remains a tantalizing scientific frontier. While the notion of "making it rain" evokes images of whimsical rainmakers, the reality is a complex interplay of atmospheric dynamics and carefully engineered interventions.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Precipitation
Precipitation, the process by which water falls from the atmosphere to the Earth’s surface, is a fundamental component of the global water cycle. It begins with the evaporation of water from oceans, lakes, and rivers, forming water vapor in the atmosphere. As this vapor rises and cools, it condenses into tiny water droplets or ice crystals, forming clouds.
Clouds are not simply collections of water droplets or ice crystals; they are dynamic systems governed by complex atmospheric processes. The formation of precipitation within clouds is a delicate balance of factors, including:
- Cloud condensation nuclei: These microscopic particles, such as dust, sea salt, and smoke, act as surfaces upon which water vapor condenses.
- Temperature: The temperature of the cloud influences the phase of water (liquid or solid) and the rate of condensation.
- Updraft: The upward movement of air within the cloud, known as an updraft, lifts water droplets or ice crystals higher into the atmosphere.
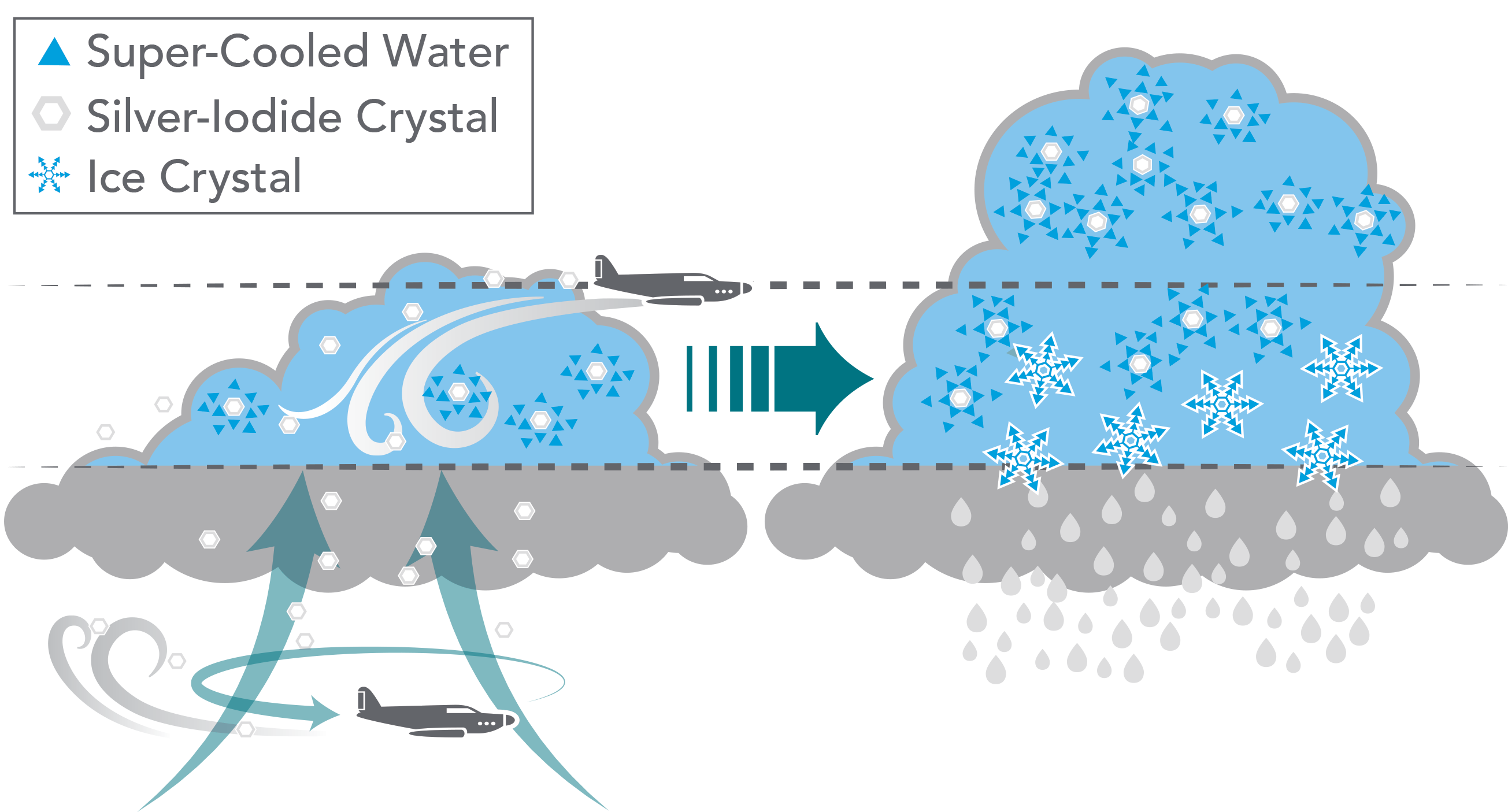
- Collision and coalescence: As water droplets collide and merge, they grow larger, eventually becoming heavy enough to fall as rain.
Cloud Seeding: A Controversial Intervention
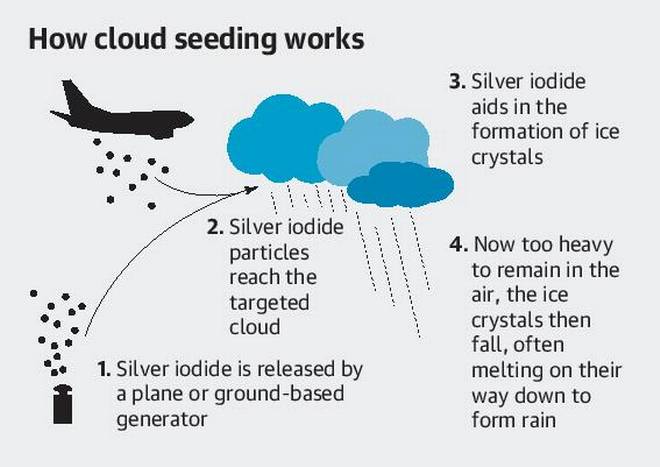
Cloud seeding, a weather modification technique, aims to enhance precipitation by introducing artificial condensation nuclei into clouds. The primary goal is to increase the number of cloud condensation nuclei, thereby promoting the formation of larger droplets or ice crystals, ultimately leading to more precipitation.
The Science Behind Cloud Seeding
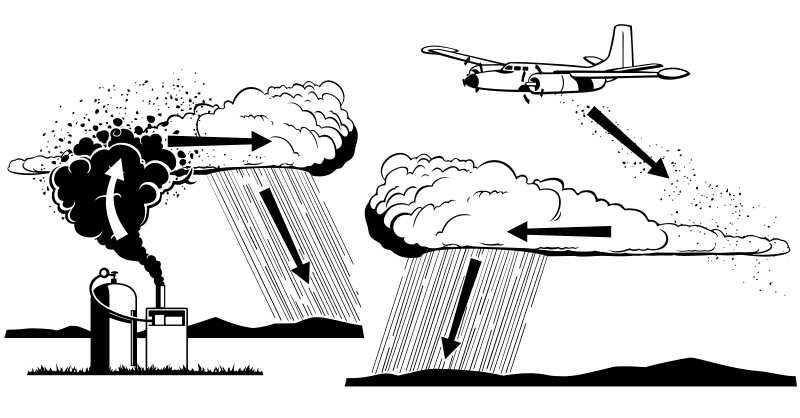
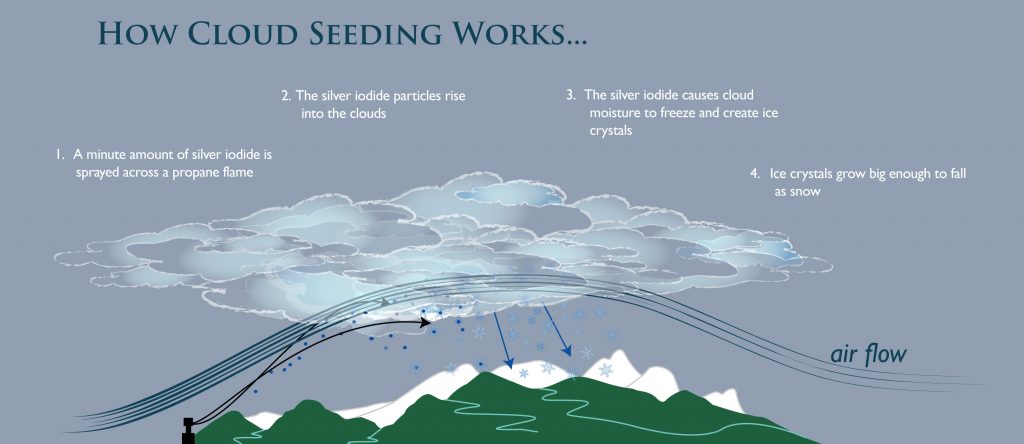
Cloud seeding typically involves dispersing seeding agents into clouds, either from the ground or through aircraft. The most common seeding agents are:
- Silver iodide: This compound, similar in structure to ice, acts as a nucleus for the formation of ice crystals, particularly in cold clouds.
- Dry ice (solid carbon dioxide): Dry ice rapidly cools the air, causing water vapor to freeze and form ice crystals.
- Hygroscopic materials (salt, sodium chloride): These materials attract water vapor, promoting the growth of water droplets in warm clouds.
The effectiveness of cloud seeding remains a subject of debate within the scientific community. While some studies have shown promising results, others have yielded inconclusive findings.
Factors Influencing Cloud Seeding Effectiveness
Several factors can influence the success of cloud seeding operations:
- Cloud type: Cloud seeding is most effective in certain types of clouds, such as cumulus congestus (towering clouds) and orographic clouds (clouds formed by air rising over mountains).
- Atmospheric conditions: The presence of sufficient moisture, updraft, and suitable temperatures are crucial for successful cloud seeding.
- Seeding agent and delivery method: The choice of seeding agent and its delivery method can significantly impact the effectiveness of the operation.
Applications and Potential Benefits of Cloud Seeding
Despite the uncertainties surrounding its effectiveness, cloud seeding has been employed for a variety of purposes, including:
- Augmenting precipitation: Cloud seeding has been used to increase rainfall in regions facing water shortages.
- Suppressing hail: Seeding can reduce the size and intensity of hailstorms, minimizing damage to crops and infrastructure.
- Dispersing fog: Cloud seeding can be used to dissipate fog, improving visibility at airports and other transportation hubs.
Environmental Considerations and Ethical Concerns
The environmental impact of cloud seeding remains an area of ongoing research. Concerns include:
- Unintended consequences: The long-term effects of introducing artificial nuclei into the atmosphere are not fully understood.
- Water rights and distribution: The potential for cloud seeding to alter precipitation patterns could lead to conflicts over water resources.
- Ethical considerations: The deliberate modification of weather patterns raises ethical questions about human manipulation of natural processes.
FAQs About Cloud Seeding
1. Does cloud seeding actually work?
The effectiveness of cloud seeding remains a subject of debate within the scientific community. Some studies have shown promising results, while others have yielded inconclusive findings. More research is needed to fully understand the impact of cloud seeding on precipitation patterns.
2. What are the risks associated with cloud seeding?
The potential risks associated with cloud seeding include unintended consequences on the environment, potential conflicts over water resources, and ethical concerns about human manipulation of natural processes.
3. How is cloud seeding regulated?
Regulations governing cloud seeding vary from country to country. In some regions, cloud seeding operations are subject to strict environmental impact assessments and public consultation.
4. What is the future of cloud seeding?
The future of cloud seeding is uncertain. Further research is needed to better understand its effectiveness, environmental impacts, and ethical implications. Advanced technologies, such as drones and artificial intelligence, could potentially enhance the precision and efficiency of cloud seeding operations.
Tips for Understanding Cloud Seeding
- Consult reputable scientific sources: Reliable information on cloud seeding can be found in peer-reviewed scientific journals and reports from reputable research institutions.
- Be critical of anecdotal evidence: Anecdotal accounts of cloud seeding success should be evaluated with caution, as they may not reflect scientific rigor.
- Consider the ethical implications: The deliberate manipulation of weather patterns raises important ethical considerations that should be carefully considered.
Conclusion
Cloud seeding represents a complex and evolving field of weather modification. While it holds potential for addressing water shortages and mitigating the effects of extreme weather events, its effectiveness, environmental impacts, and ethical implications require careful consideration and ongoing research. As our understanding of atmospheric processes and technologies continues to advance, the future of cloud seeding remains a fascinating and potentially transformative area of scientific exploration.

.png?itok=EjbZBhpm)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Cloud Seeding Conundrum: A Scientific Exploration of Weather Modification. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!