The Indispensable Role of Sunscreen in Skin Health: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: The Indispensable Role of Sunscreen in Skin Health: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Indispensable Role of Sunscreen in Skin Health: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Indispensable Role of Sunscreen in Skin Health: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Indispensable Role of Sunscreen in Skin Health: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding the Science Behind Sunscreen
- 3.2 The Benefits of Sunscreen: Beyond Sunburns
- 3.3 Addressing Common Concerns About Sunscreen
- 3.4 FAQs About Sunscreen
- 3.5 Tips for Effective Sunscreen Use
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Indispensable Role of Sunscreen in Skin Health: A Comprehensive Guide

Sunlight, while a vital source of vitamin D, also carries a significant risk to skin health. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation, specifically UVA and UVB rays, can penetrate the skin, causing damage that manifests in various ways, from immediate sunburn to long-term consequences like premature aging and skin cancer. This is where sunscreen, a crucial element of a comprehensive skincare routine, plays a vital role in protecting the skin from the harmful effects of the sun.
Understanding the Science Behind Sunscreen
Sunscreens function by absorbing or reflecting UV radiation before it reaches the skin. They contain active ingredients that either absorb UV rays and convert them into heat, or physically block them from penetrating the skin.
Types of Sunscreen:
- Chemical Sunscreens: These absorb UV rays and convert them into heat, preventing them from reaching the skin. Common chemical filters include oxybenzone, avobenzone, octinoxate, and octisalate.
- Physical Sunscreens: These act as a physical barrier, reflecting UV rays away from the skin. The most common physical filters are zinc oxide and titanium dioxide.
Sun Protection Factor (SPF):
SPF measures a sunscreen’s ability to protect against UVB rays, which are primarily responsible for sunburn. A higher SPF indicates a greater level of protection. For example, an SPF 30 sunscreen filters out approximately 97% of UVB rays, while an SPF 50 sunscreen filters out 98%. However, it is important to note that no sunscreen can block 100% of UV rays.
Broad Spectrum Protection:
Sunscreens with broad-spectrum protection offer protection against both UVA and UVB rays. UVA rays are responsible for premature aging, while UVB rays cause sunburn. It is crucial to choose sunscreens that provide broad-spectrum protection for comprehensive skin safety.
The Benefits of Sunscreen: Beyond Sunburns
While preventing sunburn is a primary benefit, sunscreen offers a range of advantages for maintaining healthy skin:
- Reduces the Risk of Skin Cancer: Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer, and prolonged sun exposure is a major risk factor. Sunscreen significantly reduces the risk of developing all types of skin cancer, including melanoma, the deadliest form.
- Prevents Premature Aging: UV radiation breaks down collagen and elastin, the proteins responsible for skin elasticity and firmness. This leads to wrinkles, fine lines, age spots, and uneven skin tone. Sunscreen helps prevent these signs of aging by protecting the skin from UV damage.
- Protects Against Hyperpigmentation: Sun exposure can trigger the production of melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. This can lead to dark spots, freckles, and uneven skin tone. Sunscreen helps prevent hyperpigmentation by limiting melanin production.
- Improves Skin Conditions: For individuals with certain skin conditions like acne, rosacea, or eczema, sun exposure can exacerbate symptoms. Sunscreen helps protect the skin and reduce inflammation, potentially improving the condition.
Addressing Common Concerns About Sunscreen
Despite its numerous benefits, some misconceptions surround sunscreen use. Here, we address some common concerns:
1. Sunscreen is harmful to the environment:
While some chemical sunscreen ingredients like oxybenzone and octinoxate have been linked to coral bleaching, research is ongoing to understand their full impact. Choosing reef-safe sunscreens with mineral filters like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide is a responsible option for both skin and the environment.
2. Sunscreen is not effective:
Sunscreens are effective when applied correctly and reapplied regularly. The amount of sunscreen used and its application frequency significantly impact its effectiveness.
3. Sunscreen is only necessary during summer:
UV rays are present year-round, even on cloudy days. It is essential to wear sunscreen daily, regardless of the season or weather conditions.
4. Sunscreen causes vitamin D deficiency:
While sun exposure is the primary source of vitamin D, most people can still obtain sufficient levels through a healthy diet and moderate sun exposure. It is crucial to strike a balance between sun protection and vitamin D intake.
FAQs About Sunscreen
Q1. What is the best SPF for everyday use?
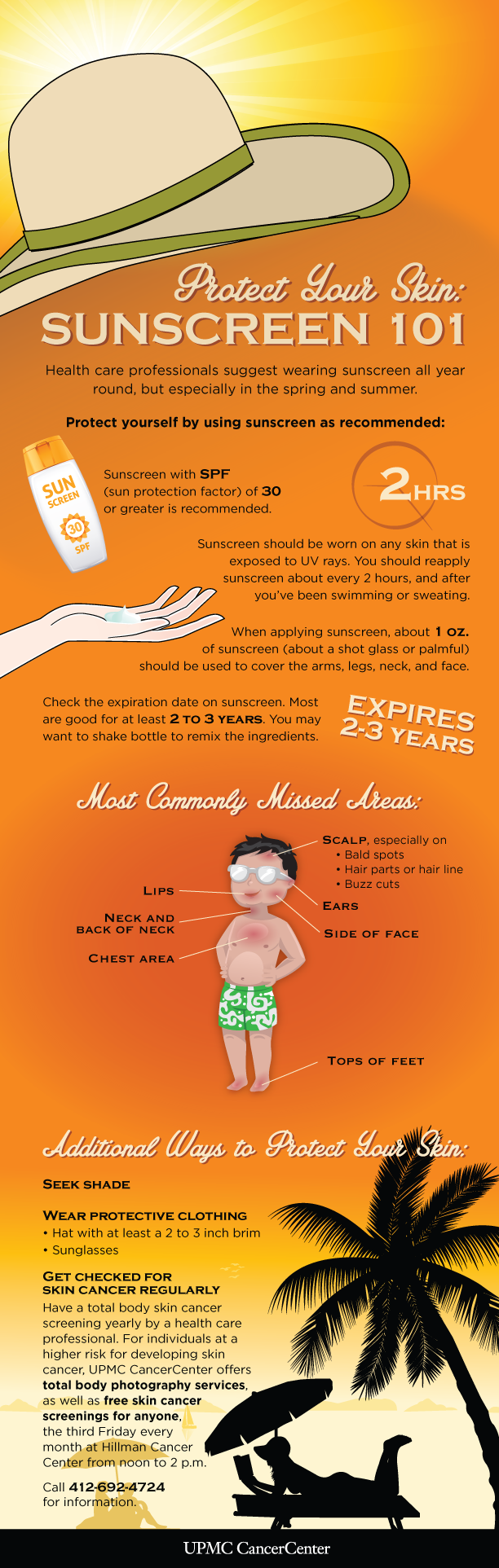
A1. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher for daily use.
Q2. How much sunscreen should I apply?
A2. Apply a generous amount, enough to cover the entire exposed area of skin. Aim for a shot glass full for the entire body.
Q3. How often should I reapply sunscreen?
A3. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, especially after swimming, sweating, or toweling off.
Q4. Can I use sunscreen on my face?
A4. Yes, there are many sunscreens specifically formulated for the face. Look for lightweight, non-comedogenic formulas that won’t clog pores.
Q5. Is sunscreen safe for babies and children?
A5. It is crucial to protect babies and children from the sun. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, and avoid exposing them to direct sunlight during peak hours.
Tips for Effective Sunscreen Use
- Apply liberally and evenly: Don’t skimp on the amount. Apply a generous layer to all exposed skin.
- Reapply every two hours: Sunscreen effectiveness diminishes over time, so reapplication is essential, especially after swimming, sweating, or toweling off.
- Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen: Ensure your sunscreen protects against both UVA and UVB rays.
- Use a sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher: This level of protection is recommended for daily use.
- Apply sunscreen 20 minutes before sun exposure: This allows the sunscreen to absorb into the skin and become effective.
- Wear protective clothing: Cover up with hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeved shirts and pants to minimize sun exposure.
- Seek shade during peak hours: Avoid direct sunlight between 10 am and 4 pm when UV rays are strongest.
- Check the expiration date: Sunscreens lose their effectiveness over time, so check the expiration date and replace them as needed.
- Store sunscreen properly: Keep sunscreen in a cool, dry place, out of direct sunlight.
Conclusion
Sunscreen is an essential tool for protecting skin health and preventing the harmful effects of UV radiation. By incorporating sunscreen into your daily skincare routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of sunburn, skin cancer, premature aging, and other skin problems. Choosing a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, applying it liberally and reapplying it regularly, and adopting other sun protection measures are crucial for maintaining healthy and radiant skin. Remember, protecting your skin from the sun is an investment in your long-term health and well-being.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Indispensable Role of Sunscreen in Skin Health: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!