Unveiling the Complexity of Human Skin: A Journey into the World of 3D Models
Related Articles: Unveiling the Complexity of Human Skin: A Journey into the World of 3D Models
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Complexity of Human Skin: A Journey into the World of 3D Models. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Complexity of Human Skin: A Journey into the World of 3D Models
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Complexity of Human Skin: A Journey into the World of 3D Models
- 3.1 The Power of Visualization: 3D Models as a Window into Skin Biology
- 3.2 Building the Model: Techniques and Technologies Shaping Skin 3D Models
- 3.3 The Future of Skin 3D Models: Pushing the Boundaries of Understanding
- 3.4 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Human Skin 3D Models
- 3.5 Tips for Effective Use of Human Skin 3D Models
- 3.6 Conclusion: A New Era of Skin Understanding
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Complexity of Human Skin: A Journey into the World of 3D Models

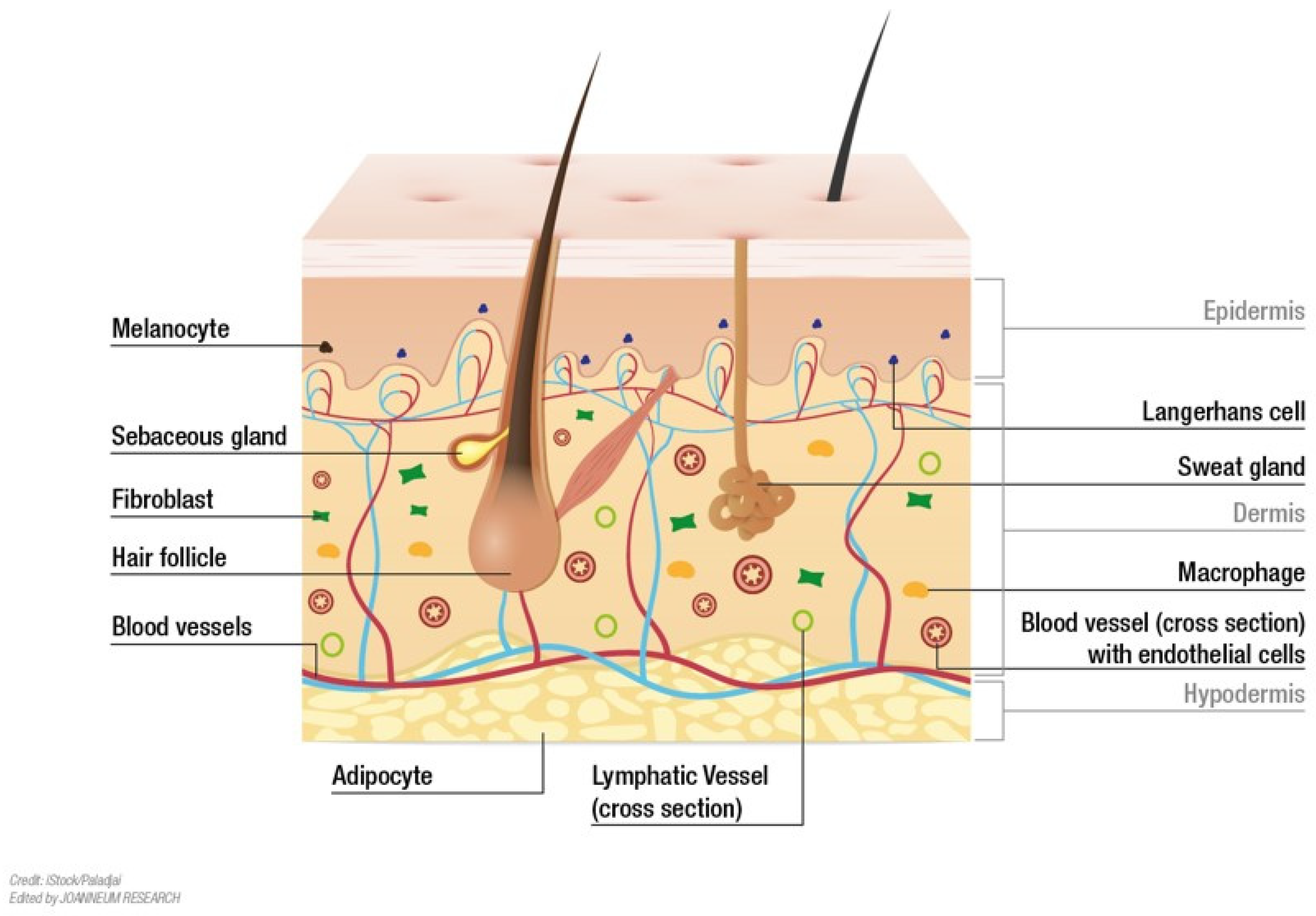
The human skin, our largest organ, serves as a protective barrier, a sensory interface, and a vital component of our overall health. Its intricate structure, composed of multiple layers and diverse cell types, has fascinated scientists and researchers for centuries. However, understanding the intricacies of this complex organ has historically been limited by the challenges of studying a three-dimensional structure in a two-dimensional space. The advent of 3D modeling has revolutionized this field, offering unprecedented insights into the anatomy, physiology, and pathology of human skin.
The Power of Visualization: 3D Models as a Window into Skin Biology
3D models of human skin provide a unique and powerful tool for visualizing and understanding the intricate structure and function of this vital organ. They offer a level of detail and interactivity that traditional two-dimensional representations cannot achieve, enabling researchers, educators, and clinicians to:
- Explore the Skin’s Layered Architecture: 3D models accurately depict the different layers of the skin, including the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous fat, showcasing their unique cellular composition and interconnections. This allows for a deeper understanding of how each layer contributes to the skin’s overall function.
- Visualize Cellular Processes: 3D models can illustrate the intricate cellular processes within the skin, such as keratinocyte differentiation, melanocyte pigment production, and fibroblast collagen synthesis. This provides a visual representation of the dynamic interactions between different cell types and their roles in maintaining skin health.
- Study Skin Diseases and Conditions: 3D models are invaluable for studying various skin diseases and conditions. They can depict the structural changes associated with conditions like psoriasis, eczema, and skin cancer, providing a visual understanding of their pathogenesis and potential therapeutic targets.
- Develop and Test New Treatments: 3D models serve as a platform for testing new drugs, therapies, and cosmetic products. By simulating the skin’s response to different treatments, researchers can optimize their development and predict their potential efficacy and safety.
- Educate and Engage Audiences: 3D models provide an engaging and interactive way to educate students, patients, and the general public about the structure, function, and health of human skin. Their visual nature enhances understanding and promotes awareness of skin health and disease prevention.
Building the Model: Techniques and Technologies Shaping Skin 3D Models
The creation of accurate and detailed 3D models of human skin relies on a combination of advanced technologies and techniques:
- Micro-CT Scanning: This non-invasive imaging technique uses X-rays to create detailed 3D images of the skin’s internal structure. Micro-CT scanning provides high-resolution data, allowing for the reconstruction of the skin’s complex layers and cellular organization.
- Confocal Microscopy: This technique uses lasers to illuminate thin slices of skin tissue, generating high-resolution images of the skin’s cellular structures and their interactions. Confocal microscopy data can be used to create 3D models that depict the distribution and arrangement of different cell types within the skin.
- Electron Microscopy: This technique uses electron beams to create highly magnified images of the skin’s ultrastructure, revealing the intricate details of cellular organelles and their interactions. Electron microscopy data provides valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying skin function and disease.
- 3D Printing: This technology allows for the creation of physical models of the skin based on digital 3D data. 3D printed models provide a tangible representation of the skin’s structure, allowing for hands-on exploration and analysis.
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software: CAD software is used to create and manipulate 3D models of the skin based on data obtained from various imaging techniques. This software allows for the creation of highly detailed and realistic 3D models that can be used for research, education, and clinical applications.
The Future of Skin 3D Models: Pushing the Boundaries of Understanding
The field of 3D modeling is constantly evolving, with ongoing advancements in imaging technologies, computational power, and data analysis techniques. These advancements are leading to the development of increasingly sophisticated and realistic 3D models of human skin, offering new opportunities for:
- Personalized Medicine: 3D models can be customized to represent individual patients’ skin characteristics, allowing for personalized diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies.
- Disease Modeling: 3D models can be used to create realistic representations of specific skin diseases, enabling researchers to study their pathogenesis and develop targeted therapies.
- Drug Discovery and Development: 3D models can be used to test the efficacy and safety of new drugs and therapies, accelerating the development of new treatments for skin diseases.
- Cosmetic Research: 3D models can be used to study the effects of cosmetic products on the skin, leading to the development of more effective and safer products.
- Virtual Reality Applications: 3D models can be integrated into virtual reality environments, providing immersive and interactive experiences for education, training, and patient engagement.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Human Skin 3D Models
Q: What are the limitations of 3D models of human skin?
A: While 3D models offer significant advantages, they also have limitations. They cannot fully replicate the complex dynamic processes of living tissue, such as blood flow, nerve conduction, and immune responses. Additionally, the accuracy of the model depends on the quality of the data used for its construction, and current technologies may not capture all aspects of skin structure and function.
Q: How are 3D models of human skin used in clinical practice?
A: 3D models are increasingly being used in clinical practice for various purposes, including:
- Diagnosis: 3D models can help clinicians visualize the extent and severity of skin conditions, facilitating accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Treatment Planning: 3D models can aid in planning surgical procedures, such as skin grafts and reconstructive surgeries, by providing a detailed visualization of the affected area.
- Patient Education: 3D models can be used to explain complex skin conditions to patients, enhancing their understanding and engagement in their treatment.
Q: What are the ethical considerations surrounding the use of 3D models of human skin?
A: The use of 3D models of human skin raises ethical considerations related to data privacy, informed consent, and the potential misuse of the technology. Researchers and clinicians must ensure that the use of 3D models is ethically sound and respects the rights and privacy of individuals involved.
Tips for Effective Use of Human Skin 3D Models
- Choose the Right Model: Select a 3D model that is appropriate for your specific research or clinical needs, considering the level of detail, accuracy, and functionality required.
- Understand the Limitations: Be aware of the limitations of 3D models and avoid overinterpreting the results.
- Validate the Model: Validate the model’s accuracy by comparing its predictions with real-world data.
- Use the Model Responsibly: Use 3D models ethically and responsibly, ensuring data privacy and informed consent.
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of advancements in 3D modeling technologies and techniques to ensure the use of the most accurate and effective models.
Conclusion: A New Era of Skin Understanding
3D models of human skin represent a significant advancement in our understanding of this complex organ. They provide a powerful tool for visualizing, studying, and understanding the intricate structure, function, and pathology of the skin. As 3D modeling technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated and realistic models that will revolutionize our approach to skin health, disease, and treatment. This technology holds immense promise for advancing research, improving clinical practice, and ultimately enhancing our understanding of the vital role human skin plays in our overall health and well-being.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Complexity of Human Skin: A Journey into the World of 3D Models. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!